Does India’s diaspora mask the contradictions and inequalities within, or is it the nation’s most potent catalyst for change beyond borders?
Before we go there, the context…
In the age of global clout and soft power, India stands at a fascinating crossroads—where its superpower ambitions are often eclipsed by the dazzling success stories of its people abroad. Stretched across every continent, the Indian diaspora isn’t just a network; it’s a phenomenon that redefines influence, connecting Silicon Valley boardrooms, British parliament, Hollywood sets, and United Nations assemblies.
This article invites a provocative exploration—moving beyond the metrics of GDP and nuclear strength to ask whether India’s most significant export is not its goods but its people themselves. In a divided, ambitious, and restless nation, are global perceptions shaped more by diaspora than by domestic reality?
Let us explore.
Table of Contents
India’s Aspirations and Reality
India has long been projected as a potential superpower, based on its rapid economic growth, large population, and burgeoning technological prowess. When 2025 ends, India’s GDP is estimated to make it the world’s third-largest economy, trailing only the United States and China. Its young demographic remains a significant advantage, with a median age much lower than that of major competitors, promising a productive workforce for decades.

Yet, significant obstacles remain. Indian policymakers face deep-rooted bureaucratic inertia, patchy infrastructure, persistent inequality, and a reliance on imported oil and gas, particularly in the energy sector. Despite impressive economic forecasts and its leap ahead as one of the fastest-growing economies, India’s trade potential and internal cohesion lag behind countries like China. Execution risk, political will, and long-standing governance challenges continue to temper ambitions.
Diaspora: The “Superpower” Abroad
India’s global influence is amplified by its 35-million-strong diaspora, spread across more than 200 countries. This community generates the world’s most significant remittance inflow—$129 billion in 2024—strengthening foreign reserves and surpassing both FDI and development aid. Beyond economic support, the diaspora drives innovation and global leadership, with Indian-origin CEOs leading companies like Microsoft and Adobe. Politicians of Indian descent shape policies in the US, UK, Canada, and beyond. Their networks foster trade, open markets for Indian enterprises, and cement bilateral partnerships. Politically, they lobby for India’s interests, influencing negotiations such as the US-India nuclear deal.
US-India technology and policy cooperation has been bolstered by the influential roles of Indian-origin leaders such as Satya Nadella and Sundar Pichai, promoting strategic partnerships in IT, cloud, and AI. Additionally, political figures such as Kamala Harris and Rishi Sunak have leveraged their positions to advocate for diaspora issues, thereby strengthening India’s role in key policy negotiations and trade agreements with the US and the UK.
Business Successes and Economic Impact
Indian-origin billionaires, including Jay Chaudhry, Vinod Khosla, and Rakesh Gangwal, have significantly fostered innovation in the US and global markets while strengthening business ties with India. In Dubai, nearly a third of registered startups are founded by Indians, enhancing tech investments and ties with the UAE. Additionally, during the COVID-19 pandemic, diaspora organizations like Indiaspora raised over $15 million for relief efforts in India, showcasing transnational solidarity.
Quantitative Highlights
| Sector | Diaspora Impact(2025) |
| US Unicorn Startups | 11% of founders Indian-origin |
| US Patents | 10% held by Indian-Americans |
| US Tax Contribution | 5% of taxes by 1.5% population |
| Remittances to India | $129 billion (2024) |
| Dubai Startups | 1 in 3 Indian founders |
India’s $75 billion defense budget makes it the world’s fourth largest, with one of the most enormous standing armies (1.47 million personnel). Its Air Force and Navy showcase growing strength with Rafale jets, aircraft carriers, and submarines, while nuclear triad capability cements strategic deterrence. However, budget constraints—nearly a quarter spent on pensions—limit modernization, leaving India trailing the U.S., China, and Russia in technology and scale. Analysts suggest raising defense spending to 2.5–3% of GDP to counter regional threats and advances in AI, hypersonics, and space defense.

Diplomatic Leverage and Cultural Ambassadors
Diaspora members function as India’s informal diplomats, promoting everything from bilateral trade agreements to Indian festivals and cuisine abroad. Their cultural diplomacy—via Bollywood, yoga, festivals, and philanthropy—has deeply embedded Indian traditions in global societies. The diaspora’s reach is so strong that initiatives like declaring Diwali an official holiday in US states illustrate how Indian culture has gained widespread acceptance.
India’s government has institutionalized diaspora engagement through schemes like the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, E-Migrate platform, and the Overseas Citizenship of India card program. While other countries have embedded their diaspora into national development strategies, India’s own efforts continue to evolve, shifting from limited paternalism to active partnership.
Successful Diaspora Stories
Diaspora-Led Business Partnerships
ArcelorMittal and Tata Steel formed a significant partnership, creating a leading global steel company that enhances India’s manufacturing and job market. Additionally, Indian-origin startups such as Flipkart and Paytm have transformed the e-commerce and digital payments landscape, attracting significant investments and generating numerous jobs. Lastly, the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) has facilitated substantial bilateral investments, with UAE companies such as DP World and Lulu Group expanding into India’s logistics, retail, and real estate sectors.
Technology Transfers and Innovation
Airbus collaborates with Tata Advanced Systems to produce C295 military transport aircraft in India, aiming to enhance local aerospace capabilities and facilitate technology transfer. VinFast, a Vietnamese automaker, is investing in India, leveraging its diaspora networks to develop electric vehicle manufacturing capacity. Indian-origin scientists engaged with NASA, ISRO, and top universities participate in collaborative research projects and mentoring initiatives to strengthen India’s space technology and innovation landscape.
Political Interventions and Advocacy
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas enhances India’s political and economic ties with its diaspora, fostering development projects and FDI inflows. Indian-origin politicians in the US, UK, and Canada advocate for policies that benefit India, including defense collaboration and trade agreements. Additionally, diaspora philanthropy plays a significant role in funding hospitals, schools, and rural development, as well as aiding COVID-19 relief efforts, thus amplifying government initiatives.
India’s Homegrown Strengths
While the diaspora often dominates headlines, India’s domestic achievements are equally transformative. It is the world’s third-largest startup hub, with over 100 unicorns in fintech, edtech, and e-commerce. ISRO’s Chandrayaan-3 and Aditya-L1 have elevated India as a space power. In renewable energy, India ranks third in solar production and leads the International Solar Alliance (ISA). Digital India and UPI revolutionize payments, enabling billions of transactions monthly. These milestones highlight India’s innovation and resilience, complementing diaspora contributions to its growing global stature.
Risks and Challenges
Understanding the shortcomings is the first step to evolving policy reforms.
Brain Drain Challenges
In 2024, more than 600,000 skilled Indians emigrated, primarily to the US, UK, Canada, Australia, and the UAE, in search of improved career prospects and living conditions. Since the 2000s, over 2 million IT professionals and approximately 1 million doctors have left India, creating a significant shortfall in the healthcare and technology sectors. Annually, around 200,000 students pursue higher education abroad, with about 85% not returning, consequently draining India’s human capital and weakening innovation. The economic ramifications of this brain drain include an estimated annual GDP loss of $160 billion due to the cost of subsidized education and diminished domestic productivity and research capabilities.
Social and Governance Disconnects
A disconnect exists between the diaspora’s global success and India’s internal challenges like inequality and bureaucracy. Differing perspectives often lead to fragmented engagement and unrealistic expectations for reform. Concerns also arise over wealthy diaspora members securing foreign citizenship or “golden visas,” raising questions about loyalty and fueling tax policy debates that may drive affluent Indians abroad.
Prospects for Reverse Brain Drain and Policy Responses
India is advancing “reverse brain gain” via the VAIBHAV Summit, inviting diaspora talent into academia, startups, and innovation. Policies aim to expand higher education, upgrade research infrastructure, ease immigration for entrepreneurs, and increase R&D spending—currently at just 0.64% of GDP. However, challenges such as persistent brain drain and social disconnection remain, making systemic reforms and stronger diaspora engagement essential for India’s holistic growth and emergence as a global power.
Comparing Home and Away: Superpower vs Super Diaspora
India’s global affairs are thus shaped as much—if not more—by its people abroad as they are by policymakers at home. While domestic achievements in military strength, economic growth, and technological innovation are significant, a gap remains between aspiration and full superpower capability. Many analysts argue that India’s global image may be overinflated by the success of its diaspora rather than its domestic output alone.
The table below frames this dynamic:
| Aspect | India at Home | India Abroad (Diaspora) |
| Economic Power | Fast-growing, but with deep inequality | Most significant global remittances, tech entrepreneurship |
| Political Clout | Limited global influence, strategic caution | Lawmakers, advocates in US/UK/Canada, diplomatic leverage |
| Soft Power | Bollywood, culture, youth | Ambassadors for culture, festivals, philanthropy |
| Military Strength | Nuclear power, recent assertiveness | N/A |
Brain Drain vs. Brain Gain
India faces a significant outflow of skilled professionals, with over a million doctors and two million IT specialists emigrating since the 2000s. However, this narrative includes a positive aspect, as an increasing number of returning entrepreneurs, scientists, and investors are bringing their global expertise back to enhance India’s economy.
Initiatives like the VAIBHAV Summit connect diaspora researchers with Indian universities and labs, thereby strengthening innovation in areas such as space, healthcare, and AI. Similarly, startup founders trained abroad are leveraging international experience to build ventures in India’s thriving tech ecosystem. Diaspora-led investments in fintech, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure are also helping to close gaps in capital and technology.
Superpower Question: Policies vs People
Does India’s diaspora success compensate for domestic challenges? Critics argue that global prestige derived from diaspora achievements, migration, and remittances cannot fully substitute for robust governance, equitable development, and comprehensive policy success at home. India’s international ambitions require more than backing from its “super diaspora”—they depend on sustained, strategic internal reform.
Limits and Drawbacks of Diaspora-Driven Development
Economic Vulnerabilities: Many diaspora members, especially in low-skilled jobs in the Gulf and Southeast Asia, face job insecurity, labor exploitation, and income disparity, limiting their full potential contribution to India’s development.
Social and Cultural Disconnect: There is often a gap between the successes of diaspora communities abroad and internal Indian realities, such as inequality and bureaucratic inefficiencies. Generational shifts within diaspora communities also challenge sustained cultural identity and engagement with India’s evolving socio-political landscape.
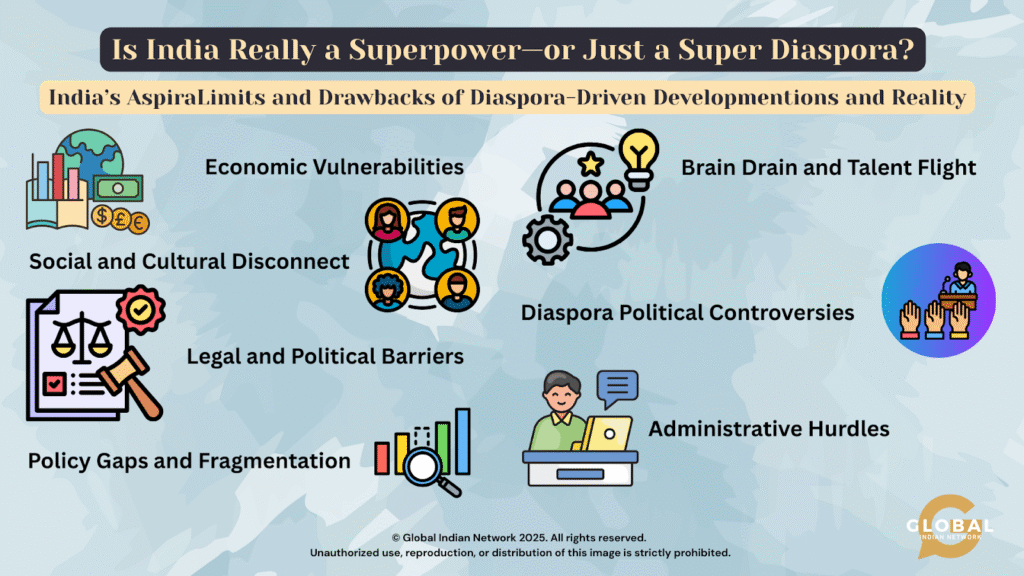
Legal and Political Barriers: Stricter immigration rules in host countries and India’s inability to provide dual citizenship restrict diaspora political participation and complicate legal status, reducing their full potential as bridges between India and the world.
Policy Gaps and Fragmentation: India’s diaspora policies remain fragmented with poor grievance redressal mechanisms, a lack of a centralized diaspora database, and selective engagement that often excludes low-income or less visible diaspora sections.
Brain Drain and Talent Flight: The continued emigration of highly skilled professionals raises concerns about India losing vital human capital necessary for internal growth and innovation, partially offsetting the benefits of the diaspora.
Diaspora Political Controversies: Some diaspora groups have been linked to divisive or separatist politics, creating diplomatic challenges and internal tensions for Indian governance.
Administrative Hurdles: Complex regulatory frameworks, bureaucratic delays, and regulatory compliance for diaspora-led investments and philanthropy discourage transparent and efficient contributions to India’s development.
These challenges suggest that, although the diaspora significantly contributes to India’s global influence and development, effective policymaking must consider the various limitations and socio-political complexities to achieve sustainable and inclusive engagement with the diaspora.
Current Policy
India’s policy blueprint for domestic transformation centers on structural reforms and inclusive development. The approach emphasizes deregulation and digital governance to streamline bureaucracy, fiscal reforms for a broader tax base, and targeted investments in infrastructure and manufacturing to spur long-term growth. Education and vocational training, labour reforms, expanded welfare programs, and strengthened public-private partnerships are also prioritized to ensure job creation, social inclusivity, and sustainable progress. Critical sectors like renewable energy, digital infrastructure, and MSMEs are targeted for transformation, while diaspora resources are mobilized for investment, knowledge transfer, and national development.
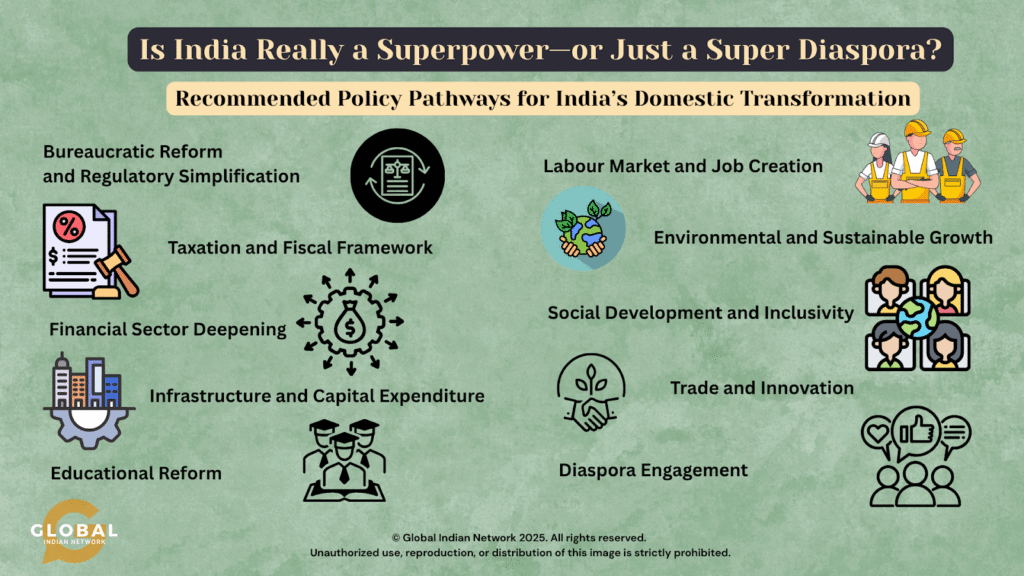
Recommended Policy Pathways for India’s Domestic Transformation
We recommend a policy framework that can iron out the gaps.
- Bureaucratic Reform and Regulatory Simplification: Overhaul bureaucratic procedures and regulatory frameworks using digital governance and a deregulation commission to increase government transparency and efficiency.
- Taxation and Fiscal Framework: Implement a modernized tax code and restructure GST/customs to broaden the tax base and support easier compliance for MSMEs.
- Financial Sector Deepening: Enhancing the domestic debt market and broadening financing options necessitate regulatory changes and improved access to credit. Liberalizing Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policies by raising sectoral caps and promoting an “Ease of Doing Business” framework can attract international capital and technology.
- Infrastructure and Capital Expenditure: Prioritize investment in infrastructure—including highways, ports, railways, and digital networks—for long-term growth and employment generation.
- Educational Reform: Reform education by expanding vocational and STEM training, updating curricula, and encouraging collaboration with global diaspora experts.
- Labour Market and Job Creation: Update labour laws for formalization and incentivize hiring, especially in labour-intensive sectors like textiles and agribusiness.
- Environmental and Sustainable Growth: Foster public-private partnerships to build climate-resilient, sustainable infrastructure and expand access to services.
- Social Development and Inclusivity: Strengthen social inclusion through welfare, skill programs, affordable healthcare, housing, and digital access for marginalized groups.
- Trade and Innovation: Diversify exports, incentivize innovation, invest in renewable energy, and support clean technology for sustainable development.
- Diaspora Engagement: Enhance diaspora engagement by launching platforms for skills and investment, simplifying regulations, and encouraging knowledge transfer to boost national growth.
Policy Pathways for India’s Diaspora Leverage
Although the diaspora’s success has contributed to India’s progress, there is still more that can be done.
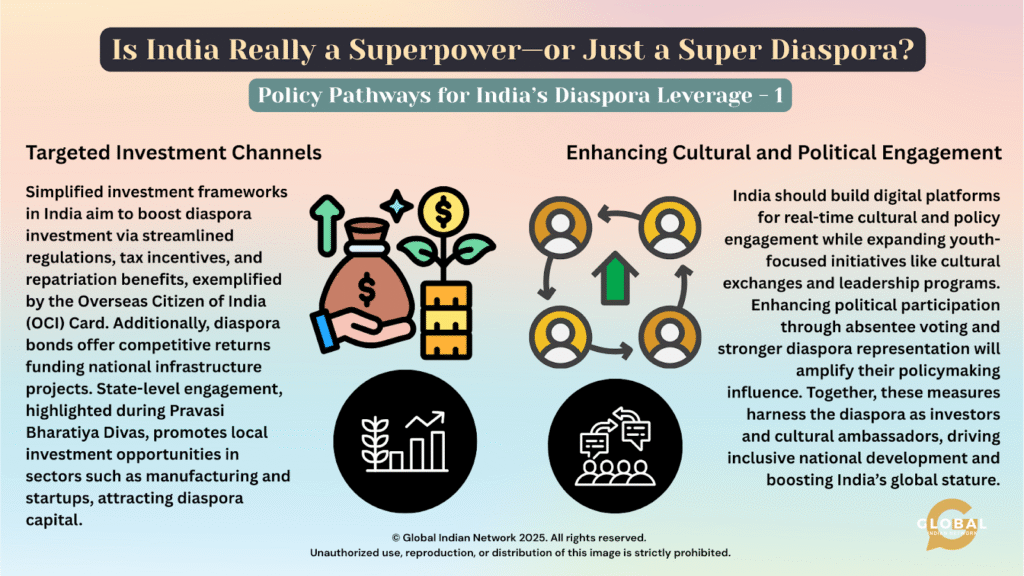
Targeted Investment Channels
India encourages diaspora investment through simplified regulations, tax incentives, and ease of repatriation. Tools like the OCI Card enable individuals to obtain lifelong visas and own property in India. Diaspora bonds attract patriotic funding for infrastructure, while events like Pravasi Bharatiya Divas highlight local opportunities in sectors such as manufacturing and startups. These efforts can be amplified.
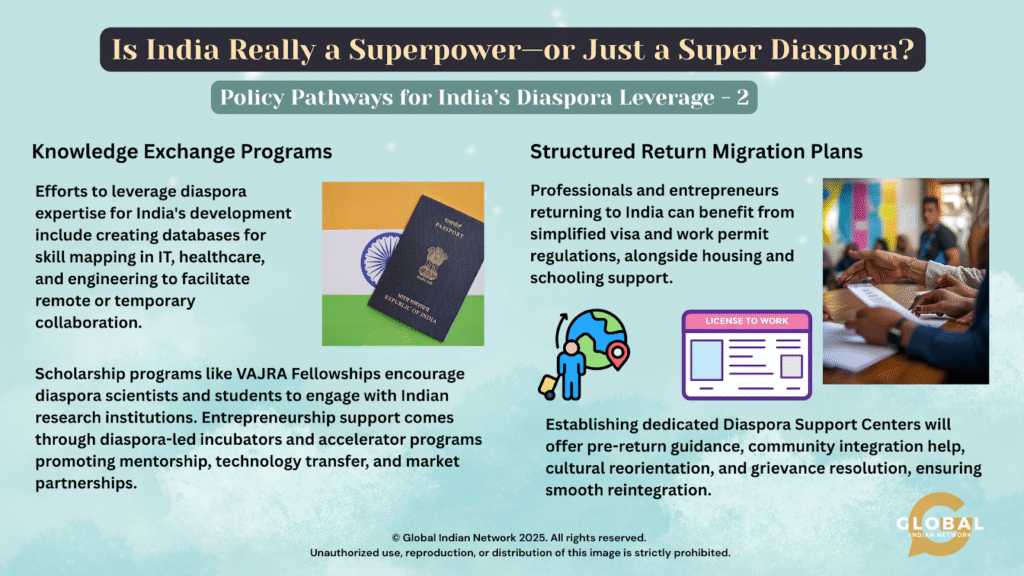
Knowledge Exchange Programs
Develop databases to identify diaspora experts in various sectors, supporting India’s development through remote collaboration and expertise. Expand scholarship and fellowship programs to engage diaspora scientists and students in Indian research. Promote entrepreneurship mentorship via diaspora-led incubators and accelerator programs, fostering startup partnerships and technology transfers.
Structured Return Migration Plans
Professionals and entrepreneurs seeking to re-enter India’s knowledge economy can benefit from streamlined visa and bureaucratic processes, as well as support for housing and education. Additionally, dedicated diaspora support centers should be established to provide pre-return guidance, assist with community integration, offer cultural reorientation, and address grievances for smoother reintegration.
Enhancing Cultural and Political Engagement
India can enhance the engagement of its diaspora through digital platforms offering real-time updates and opportunities for participation in cultural and policy dialogues. Initiatives focused on youth, such as cultural exchanges and leadership training, will foster long-term involvement. Improving political participation by streamlining absentee voting and increasing representation will empower the diaspora in policymaking. These strategies aim to utilize the diaspora as investors, knowledge partners, and cultural ambassadors, contributing to inclusive national development and strengthening India’s global position.

Conclusion
India’s diaspora is a vital asset for achieving the vision of Viksit Bharat. To capitalize on this potential, focused and inclusive policies are essential for investment, knowledge exchange, and return migration. A unified diaspora engagement framework is necessary for addressing grievances and ensuring equitable access to opportunities. Strengthening collaboration among diaspora networks can enhance India’s development. Urgent action from all stakeholders is crucial to transform India’s diaspora into a sustainable superpower, emphasizing unity, innovation, and global investment in India’s future.
India’s diaspora garners global admiration, yet domestic issues such as inequality and inadequate infrastructure remain pressing challenges. The accomplishments of Indian-origin leaders abroad may overshadow the country’s internal struggles. To maintain its status as a superpower, India must prioritise economic strength, social equity, and technological self-reliance. Without addressing these foundational issues, the disparity between India’s image and reality is likely to grow.
The question is not whether India’s people can carry its story abroad—they already do—but whether the nation itself can rise to match the brilliance of its global citizens. The actual superpower test still lies at home.
If India aligns domestic reforms with diaspora engagement, it could achieve sustainable superpower status by 2047.
Follow us as we bring you hidden tales of our proud Indians. Tomorrow, that could be you.









