Blockchain technology is the key underpinning of many digital trends in recent years, most notably cryptocurrencies and other forms of digital currencies. However, as blockchain technology becomes commonplace and finds usage in other forms, it becomes critical to understand what it is and its various parts.
In this blog, we dive into understanding what are the three primary components in a blockchain.
Table of Contents
Concept of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has become a cornerstone of modern digital innovation. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed and immutable ledger technology that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively. This ensures transparency and security, making blockchain ledgers ideal for applications such as financial transactions through digital wallets, supply chain management, and even voting systems.
A blockchain's primary purpose is to facilitate secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. It achieves this by using cryptographic techniques and a consensus mechanism to validate transactions and maintain the ledger's integrity. Understanding what are the three primary components in a blockchain is crucial for grasping how this technology works. These core components include the block, the chain, and the network. Each plays a vital role in ensuring the blockchain's functionality and security.
YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN: The Rise of Slovenia in Global Commerce: Blockchain and Beyond with Igor Jakomin
What are the Three Primary Components in a Blockchain?
The Block
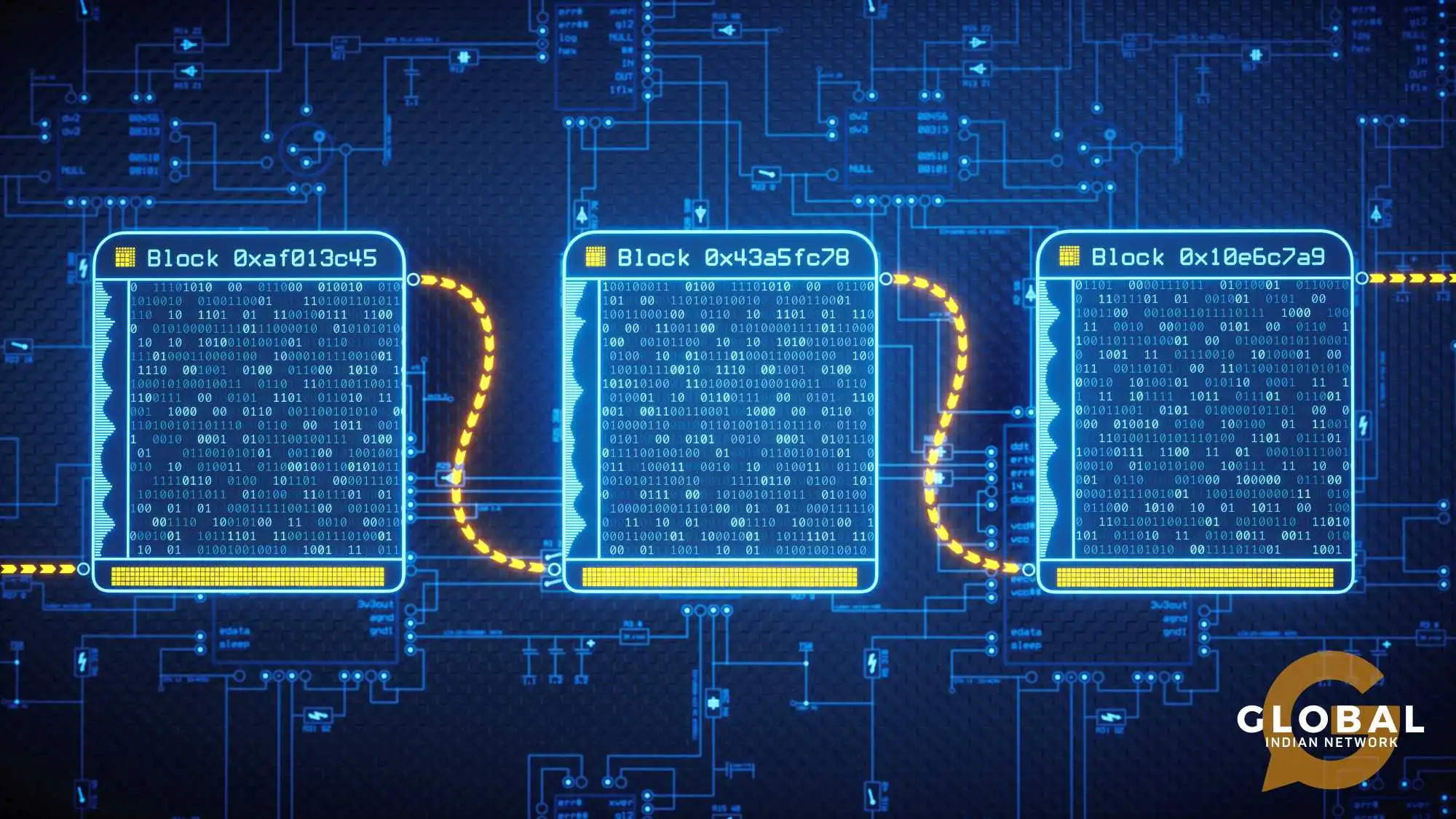
The fundamental unit of a blockchain project is the block. Each block acts as a container for transaction data and other relevant information. Blocks are added sequentially to the blockchain record, creating a continuous and chronological record of all transactions.
A block comprises three main parts: the header, the transaction data, and the nonce. The header contains metadata such as the block's hash, a timestamp, and the previous block's hash. This metadata is crucial for linking blocks together securely. The transaction data section lists all transactions recorded in the block, each encrypted to maintain confidentiality and integrity. Finally, the nonce is a random number used in cryptographic hash functions, playing a critical role in the mining process, which involves solving complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the chain.
The Chain
The chain in blockchain architecture refers to the sequential linking and chain of blocks. Each block contains a hash that uniquely identifies it and a reference to the hash of the previous block. This linking process ensures that the blockchain is chronological and immutable.
Blocks are linked through their hashes. Each current block's header contains a reference to the previous block's hash, creating a chain that can be traced back to the very first block, known as the genesis block. This structure is fundamental to the integrity of the blockchain. If any block is altered, its hash changes, breaking the link to the subsequent block and making tampering evident. This immutability is a significant advantage of blockchain technology, providing a secure and reliable record of transactions that is resistant to fraud and unauthorized modifications.
The Network
The network is the third key component of a blockchain. A blockchain platform consists of multiple interconnected nodes, individual devices or computers that maintain the blockchain. This decentralized network structure is crucial for the security, transparency, and resilience of the blockchain.
Node applications in a blockchain network play various roles. Full nodes store a complete copy of the blockchain solutions and are responsible for validating transactions and blocks. These nodes are essential for maintaining the network's integrity and security. Light nodes, or lightweight nodes, store only the block headers and rely on full nodes for transaction verification, making them less resource-intensive. Mining nodes perform the computational work required to add new blocks to the blockchain. They solve cryptographic puzzles to validate and add transactions, a process known as mining and are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts.
The decentralized nature of the network ensures that no single entity has control over the entire blockchain. This decentralization is a key feature that enhances the security and trustworthiness of the blockchain. When a new block is added, it is propagated across the network, and each node updates its copy of the blockchain, ensuring consistency and synchronization across the entire network.
ALSO READ: How is Blockchain Different from Traditional Database Models? Differences You Need to Know
Conclusion
Understanding what are the three primary components in a blockchain—the block, the chain, and the network—provides an understanding of how this technology operates. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the security, transparency, and immutability of the blockchain. The block serves as the container for transaction data, the chain links these blocks in chronological order, and the network of nodes maintains and validates the blockchain in a decentralized manner.
Blockchain technology continues to evolve, offering transformative solutions across various industries. Its ability to provide secure, transparent, and tamper-proof records makes it an invaluable tool in the digital age. Whether you are a developer, an investor, or simply a technology enthusiast, understanding the impact of blockchain technology and blockchain adoption is essential for navigating the future of digital transactions and data security.
FAQs
What are the Three Main Properties of Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology has three main properties: decentralization, immutability, and transparency. Decentralization eliminates the need for a central authority by operating on a distributed network of nodes. Immutability ensures that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, maintaining a permanent and tamper-proof ledger. Transparency allows all transactions to be publicly recorded and verified, promoting trust and accountability.
What are the Three Types of Blockchain?
The three types of blockchain are public, private, and consortium. Public blockchains are open and decentralized, allowing anyone to join and participate. Private blockchains are restricted to specific participants and offer more control over access and data. Consortium blockchains are semi-decentralized, governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity, balancing public and private blockchain features.
What are the Three Primary Components in a Blockchain?
The three primary components in a blockchain are blocks, chains, and the network. Blocks store transaction data, chains link these blocks chronologically to ensure integrity, and the network consists of nodes that maintain and validate the blockchain in a decentralized manner.










[…] Blockchain technology rapidly transforms various industries, offering enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency. As a result, blockchain development companies in India are emerging as key players in the global market. This blog will analyze the importance of blockchain technology, its growth in India, and the top blockchain companies in the country. […]
[…] blockchain is a decentralized network and a distributed and public digital ledger that aims to record […]