When Anjali Rao, an Indian-origin tech leader from Silicon Valley, returned to Bengaluru, she didn’t just come home; she stepped into the future. Leading the Global Capability Center of a Fortune 500 company, she now oversees teams building AI-driven solutions for clients across Asia, Africa, and Europe. For her, the GCC is more than a corporate hub; it’s a platform where expatriate experience meets India’s talent, creating innovations that ripple across the world.
Aarav Patel, a second-generation NRI in Toronto, mentors young AI developers in Hyderabad every Friday evening. Although he has never worked in India, these sessions provide him with a sense of belonging and purpose, connecting him to a country he primarily knows through his parents’ stories. For him, remote mentorship goes beyond volunteering; it helps him explore his role in India’s future.
Let us understand the pull factor.
Global Capability Centers (GCCs) in India have become a compelling opportunity not just for multinational corporations but also for the vibrant Non-Resident Indian (NRI), Overseas Citizen of India (OCI), and Person of Indian Origin (PIO) communities. These centers, which serve as innovation and delivery hubs for global enterprises, offer a unique nexus for NRIs to engage with India’s rapidly evolving corporate and technology landscape.
We spotlight how GCCs empower the community with opportunities for growth, leadership, and cultural reconnection. Read on.
Table of Contents
Why GCCs Matter to the Overseas Citizens
Global Capability Centers – wholly owned subsidiaries of multinational corporations – were once seen as back-office support hubs. Today, they are strategic innovation centers driving AI, digital engineering, finance, R&D, and customer experience for Fortune 500 companies. India hosts over 1,700 GCCs, employing nearly 2 million professionals, with projections indicating they will reach 3.46 million by 2030.
For the global Indian community, GCCs are not just about India’s rise in the corporate world – they are platforms to reconnect, collaborate, and invest in the country’s transformation.
Global Capability Centers are not just corporate outposts – they are the result of multinational collaboration, Indian policy support, and shared innovation ecosystems. For NRIs, OCIs, and PIOs, this means engaging with a sector that thrives on collective intelligence and global-local partnerships.
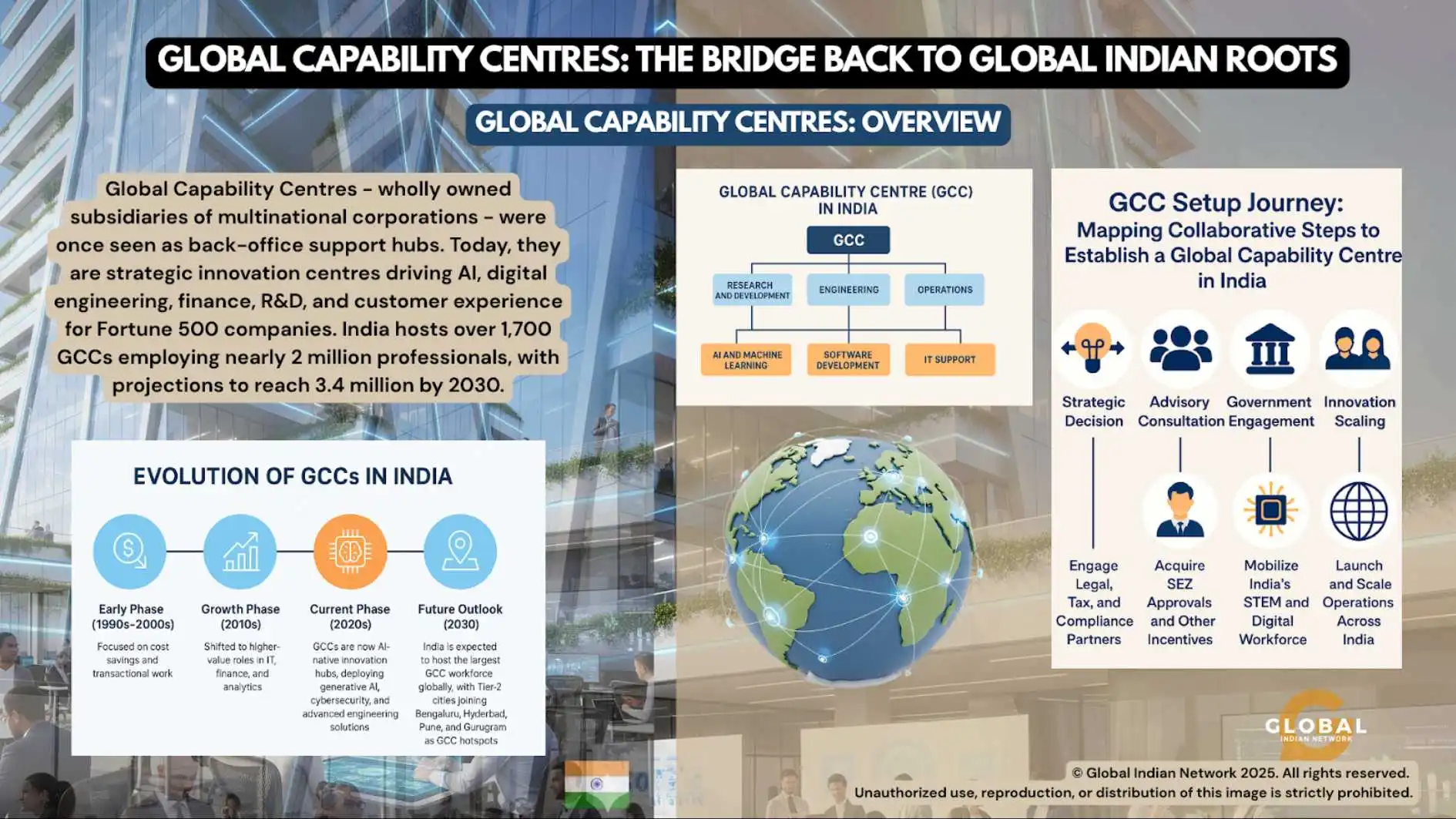
Evolution of GCCs in India
Early Phase (1990s–2000s): Focused on cost savings and transactional work.
Growth Phase (2010s): Shifted to higher-value roles in IT, finance, and analytics.
Current Phase (2020s): GCCs are now AI-native innovation hubs, deploying generative AI, cybersecurity, and advanced engineering solutions.
Future Outlook (2030): India is expected to host the largest GCC workforce globally, with Tier-2 cities joining Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, and Gurugram as GCC hotspots.

MNCs Collaborate to Set Up GCCs
Global Capability Centers in India are set up by multinational corporations (MNCs) across industries such as technology, finance, healthcare, and retail. Companies like Microsoft, Google, HSBC, Pfizer, and L’Oréal establish these wholly owned subsidiaries to manage global operations in IT, analytics, R&D, and customer experience.
The Indian government enhances economic growth through Special Economic Zones (SEZs), tax incentives, and business reforms. Advisory firms such as Deloitte and PwC aid in legal compliance. India’s skilled workforce and cost advantages attract Global Capability Centers, supported by industry forums for collaboration. Multinational corporations (MNCs) engage with Indian authorities to obtain SEZ benefits and often co-locate in tech hubs such as Bengaluru and Hyderabad, sharing infrastructure and talent. This collaborative approach facilitates efficient operations and innovation, positioning India as a preferred location for global business transformation.
Global Capability Centers – The Deep Dive
Global Capability Centers have transformed from back‑office hubs into India’s engines of global innovation. This deep dive explores how they connect multinational vision with migrant roots, driving careers, capital, and culture forward.
Impact on India’s Economy/Economic and Investment Opportunities
For Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), the GCC is an essential entry point to India’s expanding economy. Many GCCs are linked to global firms that significantly contribute to foreign direct investment (FDI) in India. By partnering with or investing in GCCs, NRIs can integrate into India’s innovation landscape. Furthermore, favorable tax arrangements between India and GCC nations, notably in the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, enable NRIs to optimize their global income, enhancing the appeal of investing in Indian GCCs.
NRIs can also participate in the growth of emerging Tier 2 cities like Kochi, Jaipur, and Coimbatore, where GCCs are expanding rapidly due to improved infrastructure and lower operating costs. This diversification beyond traditional hubs like Bengaluru and Hyderabad opens new real estate, job, and business prospects, allowing international Indian members to expand their engagement with India’s economy.
TechCircle, citing Zinnov–NASSCOM projections, reports that Tier-2 GCCs are growing at 15–20% annually, with this rate expected to rise further to around 25–30% in the following years as more global companies expand into emerging Indian cities.
- Job Creation: For every direct GCC job, one indirect job is created in allied services.
- Upskilling: GCCs drive reskilling in AI, cybersecurity, and digital engineering, transforming India’s workforce.
- Innovation Ecosystem: GCCs collaborate with Indian startups, universities, and research institutes, creating a multiplier effect.
Opportunities for NRI/OCI/PIO Professionals
- Career Re-entry: NRIs returning to India find GCCs attractive for their global work culture, competitive pay, and leadership opportunities.
- Leadership Roles: Cross-border professionals with international experience are often recruited to bridge HQs and Indian operations.
- Skill Alignment: GCCs focus on AI, fintech, biotech, and R&D – areas where expatriate expertise is highly valued.
- Networking: GCCs create ecosystems where the community professionals can mentor, advise, and collaborate with Indian talent.
Opportunities for NRI/OCI/PIO Investors
- Partnerships: GCCs collaborate with startups and service providers. Overseas entrepreneurs can plug into these networks for outsourcing, co-innovation, or supply chain integration.
- Investment Angle: GCC expansion drives demand for infrastructure, real estate, and allied services – areas where transnational investors can participate.
- Cross-Border Ventures: Migrant-led funds can co-invest in GCC-linked innovation hubs, especially in AI, green tech, and fintech.
What was once a back-office story is now a global innovation story – and Indians abroad are part of that shift.

Professional and Career Growth
India’s GCCs are recognized for cost-effective services and increasingly for high-value roles like product innovation, data science, and AI model development. NRIs in global industries can utilize GCC connections for international collaboration and knowledge exchange, enhancing career opportunities that integrate global exposure with India-based innovation, particularly benefiting younger professionals in the collective who wish to maintain links to India without full repatriation.
The rise of “nano” and “micro” Global Capability Centers (GCCs) fosters collaboration between mid-sized companies, startups, and India’s talent, offering Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) the chance to start or grow ventures aligned with Indian technology. These GCCs enable NRIs to participate in governance and management, thereby enhancing product development and compliance, improving accountability, and increasing market responsiveness. Specialized GCCs promote swift access to talent, spurring innovation in sectors like AI, fintech, healthtech, and digital engineering.

Cultural and Social Connectivity
GCCs engage NRIs and OCIs in India’s development narrative, fostering pride and contributions to the country’s transformation. They create multicultural workplaces that enhance understanding of Indian business culture and nurture social ties through philanthropy and mentorship. Additionally, GCCs help transnational leaders gain market insight within India’s innovation and regulatory frameworks, acting as brand ambassadors to navigate local nuances. This strengthens trust, opens hiring pipelines, and amplifies India’s soft power across various sectors and regions.

Government and Policy Support
India’s government actively promotes GCC growth through initiatives such as Digital India and Make in India, as well as favorable policies, including tax incentives, simplified regulatory frameworks, and infrastructure development. These measures assure NRIs that India remains a secure and competitive destination for innovation and business partnerships. Additionally, Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) status provides fast-track access to travel and business benefits, reducing friction for overseas citizens’ engagement with GCCs and related investments.
What You Should Know
India is developing a coordinated National GCC Policy to strengthen its position as the world’s leading GCC hub. CII’s proposals aim for an economic impact of $470–$600 billion and up to 25 million jobs by 2030. The framework calls for centre–state alignment, Model State GCC policies, and expansion into Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities. Supported by Zinnov–NASSCOM data, this policy aims to build distributed innovation hubs across India.
MeitY’s (Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology) evolving Digital India Act is modernizing India’s regulatory framework, providing clearer compliance pathways for data-intensive and AI-led R&D by GCCs. Initiatives like the Digital India Internship and Digital India Corporation enhance talent and collaboration. Expanded digital platforms and public procurement initiatives create new partnership opportunities, while efforts to develop tech ecosystems in Tier-2/3 cities allow GCCs to establish innovation clusters beyond major metropolitan areas.
SEZ reforms have formally enabled hybrid work, with Rule 43A allowing employees of SEZ units to work from the office or remotely, giving GCCs legal clarity for distributed delivery models. Subsequent amendments and BOA agenda notes signal long-term acceptance of hybrid operations. Legal and tax advisories confirm this flexibility, enabling GCCs to tap Tier-2 talent through satellite or nano hubs while retaining SEZ incentives and compliance benefits.
India’s Fast Track Immigration–Trusted Traveller Programme (FTI-TTP), initiated in 2024, accelerates clearance for Indian nationals and OCI holders via e-gates and pre-verification, facilitating travel for GCC experts. The program is being extended to major airports and includes pilot measures to minimize travel barriers for global talent. However, long-term employment remains subject to standard visa and FRRO procedures.
Pros and Cons of GCCs
Global Capability Centers offer strategic advantages for India and multinational corporations, but they also present challenges in innovation, talent retention, and long-term ecosystem impact.
Pros of GCCs
- Strategic Innovation Hubs: GCCs have evolved from cost-saving back offices to centers driving AI, analytics, and product development.
- Employment Generation: Over 1.6 million professionals are employed in India’s GCCs, with projections to reach 3.4 million by 2030.
- Export Growth: GCCs contribute significantly to India’s services exports, especially in IT and financial services.
- Talent Development: They upskill Indian professionals in cutting-edge domains like cybersecurity, fintech, and biotech.
- Overseas Indians’ Engagement: GCCs offer career re-entry and leadership roles for NRIs, OCIs, and PIOs, bridging global experience with local execution.
Cons of GCCs
- Innovation Dependency: Many GCCs still rely on mandates from global HQs, limiting India’s role in creating original IP.
- Talent Drain Risks: High attrition and competition for skilled professionals can strain local ecosystems.
- Limited Local Integration: Some GCCs operate in silos, with minimal collaboration with Indian startups or academia.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating SEZ policies, data protection laws, and transfer pricing can be challenging for new entrants.
- Impact on Domestic IT Firms: GCC dominance may overshadow smaller Indian IT service providers, affecting their growth trajectory.

The Path Forward – Revitalizing India’s Global Footprint through GCCs
For many NRIs, GCCs are the easiest pathway home – professionally and emotionally.
India is recognized today as the global capital of GCCs and is expected to grow as India cements its strategy to become a digital and innovation powerhouse. These GCCs cover sectors ranging from IT services, research and development, and finance to emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and product engineering. For NRIs, this growth signals significant investment and career opportunities tied to India’s leadership in the global services industry.
What This Means for You
This section has bespoke recommendations, especially for NRI/OCI/PIO readers.
Example:
If you’re an NRI professional, look for leadership roles in AI, cybersecurity, and GCC strategy.
If you’re a founder abroad, you can partner with GCCs to outsource R&D or co-develop products.
If you’re a second-generation NRI, explore culture-bridging internships, mentorships, or soft-landing programs in GCC hubs.
The transformation of India’s GCC story – from back-office support to innovation hubs – allows the expatriate to contribute as a professional, investor, mentor, and advocate, shaping India’s future as a global innovation powerhouse.
Takeaways for Global Indians
According to Moneycontrol, India’s GCCs now operate over 6,500 global leadership roles – a 30% increase driven significantly by returning NRI professionals taking on key positions in technology, engineering, and innovation functions.
Global Indians today stand at a pivotal intersection: the world’s largest GCC ecosystem and India’s accelerating innovation landscape. For NRIs, OCIs, and PIOs, GCCs represent far more than corporate hubs – they serve as connective tissue linking global expertise with India’s next leap forward. Through GCCs, transnational professionals can:
Re-enter India’s innovation economy with global capital and expertise
GCCs offer a seamless platform for returning professionals to contribute through leadership roles, project ownership, and cross-border innovation mandates.
Invest strategically in India’s fast-growing digital and AI ecosystem
With GCCs driving demand for talent, infrastructure, and emerging technologies, Global Indians can participate as investors, founders, or ecosystem partners.
Mentor and uplift India’s next generation of tech and business leaders
GCCs create structured pathways for transnational professionals to share global best practices, offer mentorship, and influence future leadership pipelines.
Strengthen India’s position in global supply chains and digital transformation
By engaging with GCCs, Global Indians can help shape India’s role as a hub for R&D, engineering, cybersecurity, and next-gen technology development.
Global Indians have the opportunity to strengthen ties with their mother country while contributing to its development.
Conclusion: A Strategic Bridge for NRIs
Global Capability Centers are more than just corporate entities; they are vibrant nodes of economic growth, global innovation, and migrant connectivity. For NRIs, they represent an incredible opportunity to harness India’s ascendant global position. Whether through direct investment, career collaboration, or cultural engagement, GCCs offer an avenue for NRIs to participate in India’s success story in a meaningful, profitable, and future-driven way. As India continues to thrust itself onto the global digital stage, GCCs will remain a critical touchpoint, linking dynamic overseas Indian citizens to the country’s expanding horizons.
GCCs are the engines of India’s global influence. For global Indians, this is the moment to reconnect, contribute, and co-create the next wave of India’s innovation story.
At the Global Indian Network, our mission is to unite Indians spread across the world. Share this vision to achieve a better India and a better world. Spread the word.

FAQs
Do GCCs hire NRIs directly?
Yes. GCCs regularly hire NRIs directly, especially for leadership, AI, engineering, finance, and global program roles where international experience is valuable. NRIs can apply from abroad or relocate, and many GCCs also offer remote or hybrid transition options before a full move to India.
Which sectors are growing fastest?
The fastest-growing GCC sectors today are AI and data engineering, cybersecurity, fintech and digital banking, healthtech and life sciences, and product/ER&D (engineering R&D). These areas are expanding rapidly as global companies shift higher-value innovation and technical mandates to India.
What skills are in the highest demand?
The highest-demand skills in GCCs today include AI/ML engineering, data science, cloud architecture, cybersecurity, and full-stack development, as well as product management, DevOps, and digital transformation. Soft skills such as global communication, cross-cultural collaboration, and agile leadership are also highly valued in senior and hybrid roles.









