In 2024, experts highlight eight trends - cyber extortion, supply chain data governance, sustainable supply chains, AI-enabled vision systems, connected workforces, composite AI, next-generation humanoid robots, and machine customers.
Table of Contents
Technology
Technology drives economic growth by adding value to raw materials and human resources, enhancing productivity, and enabling efficient production, leading to increased output and GDP. Innovation and technological advancements drive new industries, create employment, and foster entrepreneurship.
Technology significantly impacts citizens' quality of life through improvements in healthcare, education, infrastructure, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. Medical technology enhances diagnosis, treatment, and preventive care, while digital tools make education more accessible and personalised. Infrastructure innovations improve transportation, communication, and utilities, while modern farming techniques increase food production and reduce hunger.
Technology drives structural changes in economies, such as Industry 4.0, the digital economy, and smart cities, which integrate automation, data exchange, and AI in manufacturing, e-commerce, fintech, and digital services, transforming traditional business models. Technology adoption boosts global competitiveness through R&D investments, leading to breakthroughs and innovation clusters, while digital connectivity fosters economic ties through access to information and global markets.
Listen To This Podcast: Is Slovenia the Emerging Logistics Goldmine in 2024? Insights from Natasa Pogacnik
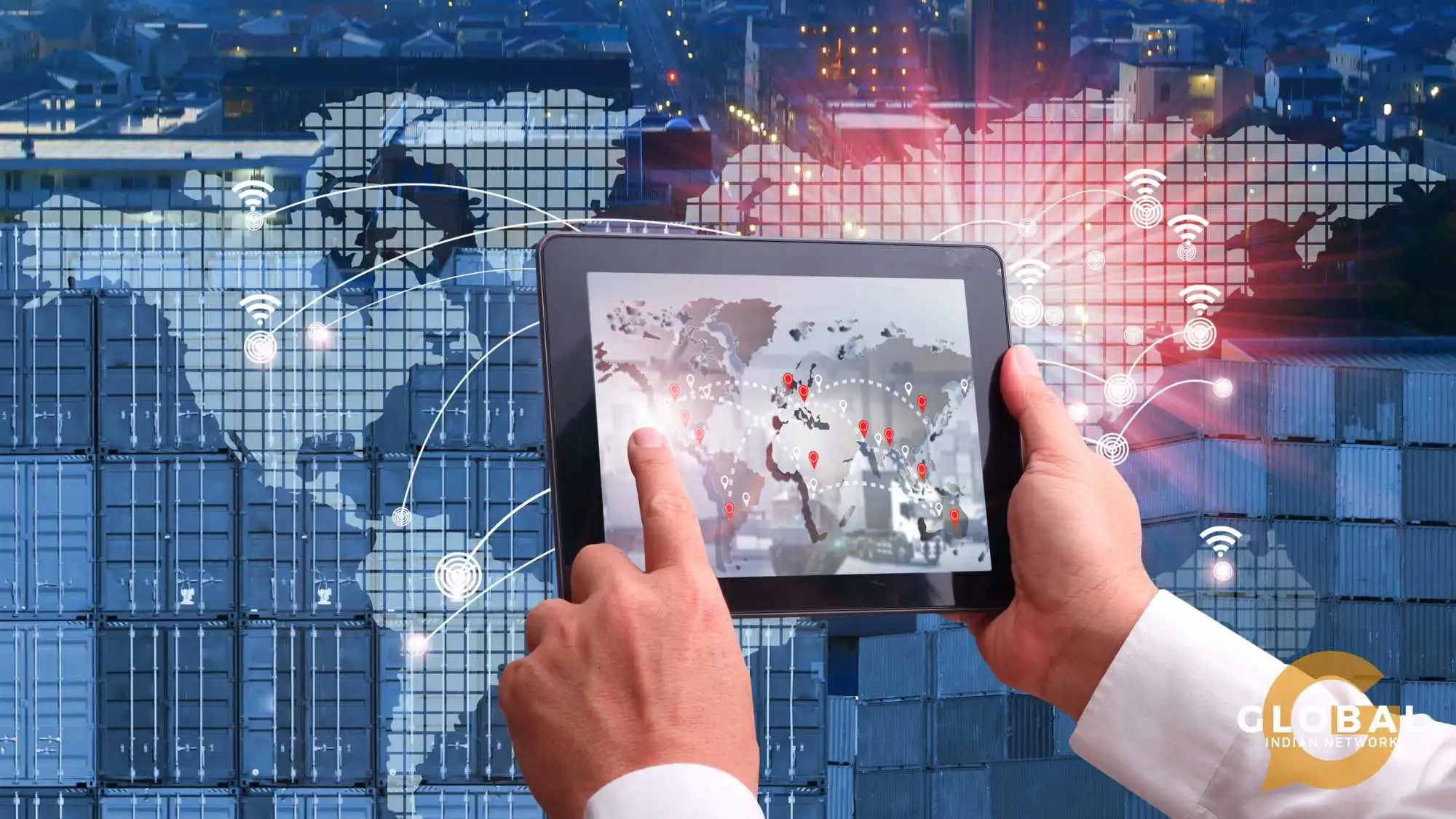
Technology Impacts Logistics
Technology has significantly transformed logistics operations, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and customer experience. Here are some key ways technology impacts the logistics industry:
Automation and Robotics: Warehouse automation enhances efficiency and accuracy in sorting, picking, and packing goods, while drones and autonomous vehicles facilitate faster last-mile delivery and lower labour costs.
IoT (Internet of Things): IoT sensors enable real-time tracking of shipments, monitoring temperature, humidity, and location, enhancing visibility. They also predict equipment failures, reducing downtime.
Big Data and Analytics: Demand forecasting and route optimisation are crucial methods used to optimise inventory levels and reduce stockouts, while algorithms help find the most efficient routes for efficient transportation.
Blockchain: Blockchain technology enhances supply chain transparency by providing secure, transparent transaction records, reducing fraud, and improving traceability.
Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms offer extensive data storage and remote access while also facilitating effective communication and coordination among stakeholders.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI models predict demand, identify patterns, and optimise supply chains, while chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer queries and streamline communication.
E-Commerce Integration: Efficient order processing is achieved through seamless integration with e-commerce platforms, while APIs connect logistics providers with online retailers.
3D Printing: 3D printing is a method that enables on-demand manufacturing by producing parts locally, thereby reducing lead times.
Green Logistics: The adoption of electric vehicles and smart packaging is a significant step towards reducing emissions and minimising environmental impact.
Cybersecurity: Data protection is ensured through robust cybersecurity measures that protect sensitive information.
In summary, technology revolutionises logistics by streamlining processes, enhancing visibility, and adapting to changing customer demands.
Challenges of Implementing Technology in Logistics
Implementing technology in logistics comes with its share of challenges. Let's delve into some of the key ones:
Customer Service and Expectations: Meeting customer expectations involves providing accurate documentation and enhancing the overall experience, and a solution is to prioritise excellent customer service to build trust, encourage repeat business, and stand out in a competitive market.
Managing Data and Technology: Modern technology adoption presents a challenge in handling massive data volumes, necessitating logistics firms to utilise software, cloud services, and smart technologies to predict customer demand, manage operations efficiently, and address supply chain crises.
Transportation Costs: The solution to managing transportation expenses, influenced by factors like fuel prices and driver shortages, is to optimise routes, utilise third-party logistics partnerships, and adopt eco-friendly vehicles.
Compliance with Laws and Standards: Navigating complex government regulations, including federal, state, local, and environmental laws, requires staying informed about changes to ensure compliance and avoid fines or operational disruptions.
IoT Implementation Challenges: The widespread adoption of IoT technology presents challenges in data security, privacy, and interoperability, necessitating the prioritisation of robust infrastructure and seamless integration of IoT devices.
ROI, Change Management, and Training: Companies face challenges in integrating new technologies due to ROI, change management, and training. To overcome these, companies should develop clear ROI metrics, effectively manage organisational change, and invest in comprehensive training programs.
In summary, while technology offers immense benefits, logistics companies must navigate these challenges strategically to thrive in a dynamic industry.
You Might Be Interested In: India and Slovenia Logistics: Business Potential in 2024
Successful Case Studies of Technology Adoption in Logistics
Let's explore some successful case studies of technology adoption in the logistics industry:
Emergence of Digitalization in Logistics and Supply Chain (L&SC): Researchers studied the evolution of digitalisation in the L&SC industry over the past 60 years, finding that it is a socially constructed phenomenon, with actor-level frameshifts contributing to an overarching "digitalisation logic" in the field.
Technology Adoption by Logistics Service Providers (LSPs): The study conducted a literature review on technology adoption by logistics service providers (LSPs) using innovation diffusion theory and absorptive capacity, revealing that understanding these strategies is crucial for improving logistics efficiency.
Researchers conducted case studies on technology adoption by LSPs, analysing ten projects by seven different firms. The findings emphasise the importance of access modes, technology type, firm characteristics, environmental context, and relationships in determining integration success.
MercuryGate's Transportation Management Success Stories: MercuryGate collaborated with three clients to improve transportation management, resulting in a streamlined supply chain, increased efficiency, cost savings, and improved service. The case studies showcase the positive impact of technology on logistics.
A retail chain utilised MercuryGate's platform for improved route optimisation, leading to over $1.5 million in savings and ensuring timely deliveries to customers, thereby enhancing efficiency and cost savings.
DHL's Technology Sector Case Studies: DHL presents real-life case studies on technology integration in logistics operations, covering topics like reverse logistics and value-added services and providing insights into successful implementation.
In summary, these case studies showcase how technology adoption drives efficiency, transparency, and competitiveness in the logistics industry.
Technology Can Help Solve Challenges in India's Logistics Sector
Technology plays a crucial role in addressing challenges within India's logistics sector. Here are some ways technology can make a positive impact:
Digital Platforms and Connectivity
Real-Time Tracking: Installing GPS-capable tracking devices allows for real-time shipment tracking. This improves visibility, reduces theft, and improves delivery accuracy.
Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors: By monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental parameters with IoT sensors, perishable commodities may be transported safely.
Blockchain: Blockchain technology increases security and transparency by reducing fraud, maintaining an immutable record of transactions, and building confidence throughout the supply chain.
Automation and Robotics
Warehouse Automation: By reducing errors and manual labour, robotic pickers, conveyor belts, and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) streamline warehouse operations.
Drones and Autonomous Vehicles: Drones can perform inventory checks, while autonomous vehicles optimise last-mile delivery while reducing costs and delivery times.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling: Route optimisation uses algorithms to analyse historical data to find efficient routes, while demand forecasting aids in resource allocation and inventory control by anticipating demand variations.
E-Commerce Integration
Marketplaces and Aggregators: Logistics processes are made easier by connecting shippers, carriers, and freight forwarders through technology platforms.
Digital freight forwarding: The efficiency of international trade is increased by online platforms that streamline online booking, paperwork, and customs clearance.
Collaborative Platforms
Sharing Economy: Collaborative logistics platforms reduce idle capacity by facilitating the sharing of resources such as delivery personnel, warehouses, and trucks.
Crowdsourced Delivery: Using locals to finish last-mile deliveries will save costs and boost productivity.
Smart Warehousing
Automated Inventory Management: Inventory levels are tracked by RFID tags and barcode scanners to prevent stockouts and overstock scenarios.
Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitor the state of the equipment, enabling timely maintenance and less downtime.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Digital India: The government's push for digitalisation encourages the use of technology in logistics.
Single Window Clearance: Streamlined license, permit, and documentation processes increase productivity.
Skill Development and Training
Upskilling Workers: Technology adoption requires a skilled labour force. Training programs can bridge the gap and increase the authority of logistics professionals.
In summary, embracing technology can revolutionise India's logistics sector, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and resilient.
Read This Article On: Business Potential of Slovenia’s Logistics Sector in 2024
Opportunities for Collaboration in Logistics Services
India and Slovenia are exploring potential collaboration in logistics services, leveraging the Port of Koper's strategic location and capabilities. Here are some key areas of potential collaboration:
Supply Chain Optimization: Indian businesses can improve their logistics and distribution networks in Europe by using the Port of Koper as a strategic entry point into Central and Eastern Europe.
Transportation and Logistics Services: Slovenian businesses are eager to work with their Indian counterparts in the transportation and logistics sectors to grow their business, with a focus on joint ventures in distribution, warehousing, and freight forwarding.
Infrastructure Development: Slovenia is presently endeavouring to enhance its aviation and rail systems, and Indian enterprises possessing specialised knowledge in these domains might be considering joint venture prospects for these initiatives.
Technology and Innovation: Slovenian businesses are well known for their creativity, expertise, dependability, flexibility, and openness to joint ventures in fields such as supply chain analytics, digital logistics, and intelligent logistics solutions.
Training and Skill Development: Knowledge sharing, cooperative training projects, and exchange programs can all promote collaboration in the logistics industry.
Collaboration opportunities may arise in various areas, but the specifics depend on the companies involved. Engaging in business networking events and dialogues can help explore these opportunities further.
Additional Reading: Business Potential of India’s Logistics Industry in 2024
Conclusion
The logistics sector is undergoing rapid global evolution due to technological advancements and supply chain uncertainties. Innovation in logistics, warehousing, and transportation is crucial and monitored by stakeholders, investors, policymakers, and economic analysts. The logistics sector, with over 166,200 companies globally, experienced a -1.28% growth in the last year, with 796,000 employees. The sector's importance in the global economy is evident, with over 31,000 patents filed and top logistics hubs in the USA, UK, India, Germany, and Canada.
India aims to enhance its standing in the Logistics Performance Index and reduce logistics costs from 13% to 8% of GDP within the next five years. Expect increased investment in technology implementation by individual logistics players and rapid innovation in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, alternate fuels, and battery technology.
In summary, the logistics industry in 2024 is at the forefront of technological innovation, with India and Slovenia playing pivotal roles. Stakeholders must embrace these advancements to ensure seamless global supply chains and sustainable growth.









[…] in Technology and Innovation: Modern technology, automation, and innovation are crucial for companies to enhance production processes, leading to […]
[…] India, and the National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture, focusing on domestic manufacturing and technology […]
[…] to introduce new processes, services, and products, with 34% implementing advanced digital technology, surpassing the EU average by 14 percentage […]
[…] aims to develop a competitive wood processing industry, supporting research, promoting advanced technologies, and producing high-value wood products, thereby enhancing the country's […]
[…] doors made of wood are gaining popularity in the construction industry as they incorporate advanced technologies to improve energy efficiency, comfort, and security in buildings. Wood is a suitable material for […]
[…] and Technology Transfer: SMEs can collaborate with larger pharmaceutical companies to enhance technology transfer and knowledge-sharing, leading to innovation and efficiency […]
[…] these issues are to be dealt with, the one theme of current-generation technology is that it can be switched off. If you get a notification on your phone while in the middle of a […]
[…] a pivotal role in ensuring products are delivered timely and cost-effectively. By optimizing logistics processes, businesses can reduce operational costs, enhance service levels, and improve overall […]
[…] logistics refers to the traditional flow of goods from manufacturers to consumers. It encompasses the entire […]