The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that from 01 January 2022 to 31 July 2024, there have been 102,997 cases and 223 deaths worldwide, across 121 countries due to Monkeypox!
| Total cases | 102 997 |
| Total deaths | 223 |
| Countries reporting cases | 121 |
| Total cases in July 2024 | 1 425 |
| Total deaths in July 2024 | 6 |
| Countries reporting cases in July 2024 | 35 |
What is Monkeypox or Mpox?
Monkeypox, also known as Mpox, is a viral disease that spreads between animals and humans. It is caused by the monkeypox virus, which is closely related to the smallpox virus. Since Monkeypox was first discovered in 1958 in monkeys, hence the name “monkeypox”.
Why is Monkeypox Concerning?
Monkeypox is concerning because it can cause severe illness in humans. Recently there has been an increase in monkeypox cases reported in several countries, including those where the disease is not recorded. This has raised concerns about the potential for a global outbreak.
Until March 2024 India has reported 30 confirmed cases of monkeypox. The exact number may change as the situation evolves.
There is no direct evidence that monsoons trigger the monkeypox situation in India. Monkeypox transmission is not dependent on seasonal factors like monsoons.
Is Mpox Dangerous and What Are Its Complications?
In some cases, it could be mild and self-limiting, while in some, it can be severe and even life-threatening. Complications of monkeypox include secondary infections, pneumonia, sepsis, loss of vision, and encephalitis.
Do We Have a Vaccine Against Monkeypox?
Yes, there are vaccines available that can help prevent monkeypox. The smallpox vaccine, Jynneos which protects against smallpox is also effective against monkeypox.
MVA-BN is a newer vaccine, that is approved in some countries to protect against monkeypox.

How does It Spread?
Monkeypox can spread through several ways:
- Direct contact with the infectious rash, scabs, or body fluids
- Respiratory secretions during prolonged, face-to-face contact or intimate physical contact
- Touching items (such as clothing or other items) of an infected person
- From infected animals, either by eating meat or using its products
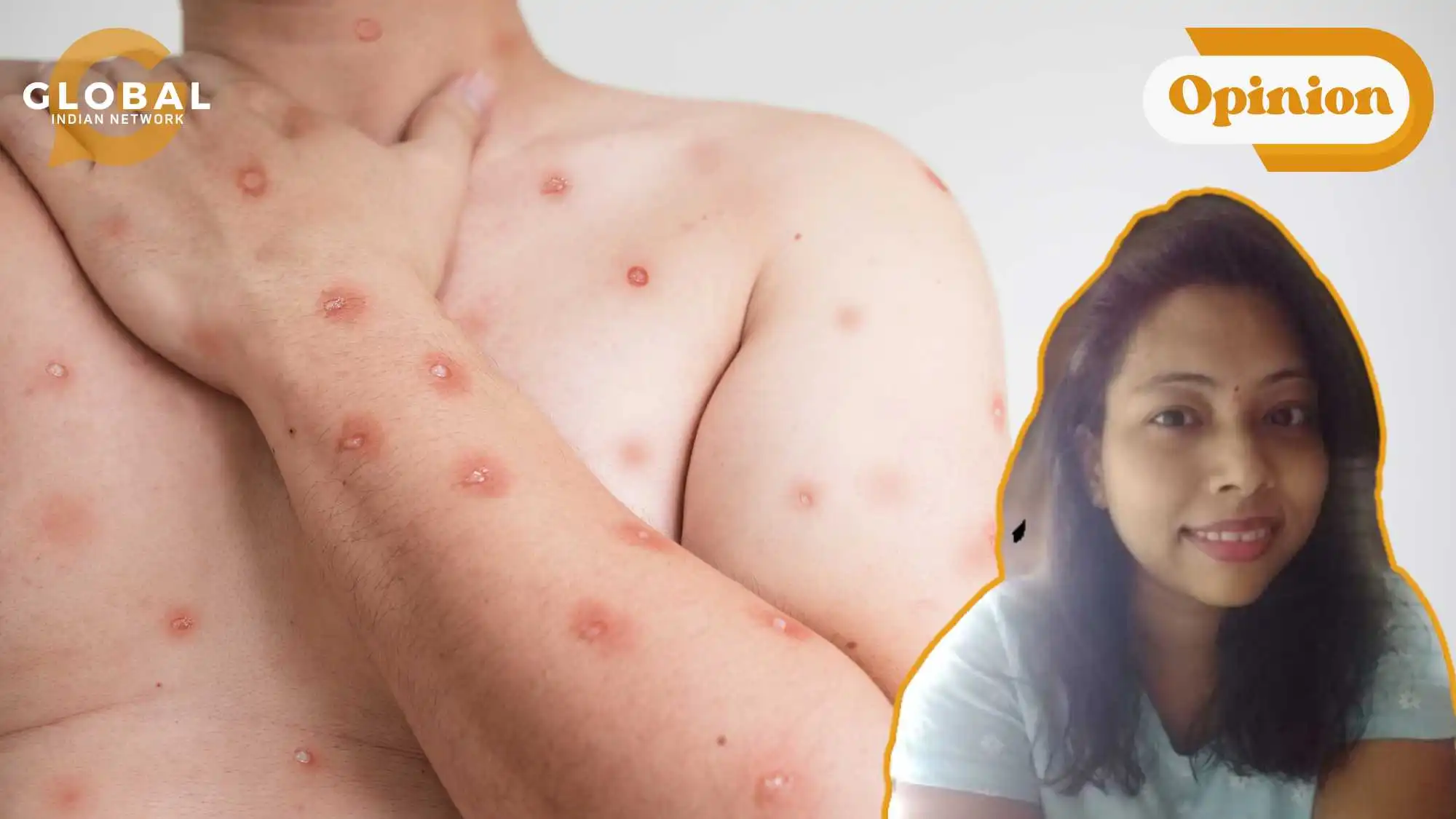
Symptoms of Monkeypox
Symptoms of monkeypox appear 6 to 13 days after exposure and can include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches and backache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Chills
- Exhaustion
- A rash that looks like pimples or blisters, on the face, inside the mouth, and on other parts of the body
How to Prevent Monkeypox?
There are several steps you can take to prevent monkeypox.
- Get Vaccinated: If you are at high risk of exposure to monkeypox, consider getting vaccinated. Talk to your healthcare provider about your eligibility and availability of the vaccine.
- Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash: Avoid close contact with people who have symptoms of monkeypox. Also, avoid contact with animals that may carry the virus, particularly in areas where monkeypox may occur.
- Avoid contact with objects and materials that a person with Mpox has used: Do not share bedding, towels, clothing, or utensils with someone who has monkeypox. Properly clean and disinfect any contaminated items.
- Wash your hands often: Wash your hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
How is Monkeypox or Mpox Diagnosed?
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests help in diagnosing monkeypox. Samples from the rash or lesions are used for testing to confirm the presence of the virus.
People with Higher Risk
Certain groups of people have a higher risk of severe illness from monkeypox
- People with weakened immune systems
- Children under 8 years old
- People with a history of eczema
- People who are pregnant or breastfeeding
How Is It Treated?
Treatment for monkeypox mainly focuses on relieving symptoms and managing complications. This may include
- Pain can be reduced by using basic medicine such as paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- Keep yourself indoors, cover your sores, and wear a mask while outdoors.
- Rinse your mouth with salt water for healing sores in the mouth
- Wash hands with soap and water frequently.
ALSO READ: Another Deadly Virus on the Rise: All You Need to Know About Mpox
Conclusion
Monkeypox is a viral disease that can cause serious illness in humans. While India has reported a few cases, there is no significant outbreak in the country at present. Getting yourself vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected people or animals can help reduce the risk of infection.
Have you air traveled recently? Are you experiencing fever or rashes on your skin? You could be exposed to monkeypox, please contact your doctor for early diagnosis and treatment.
With the rise in the number of these cases, do you think MONKEYPOX could be the next pandemic? Do let us know in the comments below.If you have interesting opinions to share do write us at larra@globalindiannetwork.com.