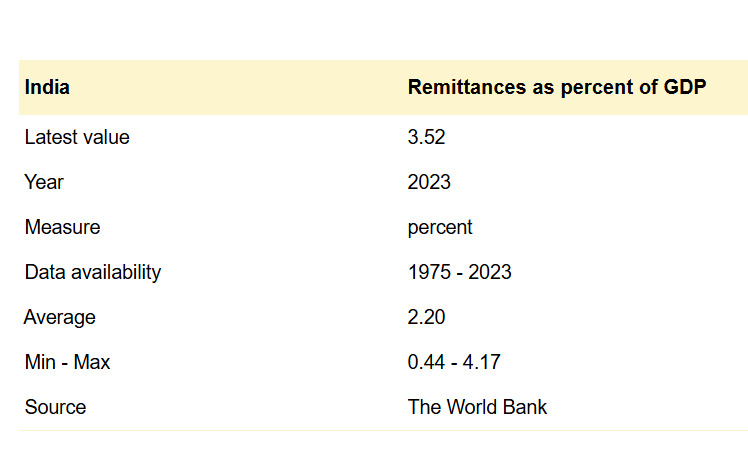In the fast-shrinking globalized world, nothing speaks more than the flow of money.
Consider this example.
When Shubhangi Sharma, an Indian microbiologist living in Berlin, organizes a grand Holi celebration for her friends, she isn’t just sharing colors—she’s also quietly demonstrating the economic power of India’s global diaspora. That €200 spent on Indian sweets and traditional clothes reverberates far beyond her Berlin home, touching artisans in Delhi markets and digital entrepreneurs who facilitate cross-border transfers.
Across continents, more than 18 million Indians channel their earnings back to their homeland, fueling a financial lifeline known as the “global Indian wallet.” The interplay of family ties, cultural celebration, and capital movement makes the global Indian wallet an extraordinary engine for India’s economic growth and transformation.
Join us in this journey to literally figure out what exactly is in the ‘global Indian wallet’ and how it influences lives—yours and mine—irrespective of residency. Let us delve into understanding how far the wallet can stretch.
Table of Contents
What is the Macro Picture?
Remittances and diaspora investments contribute significantly to India’s economic stability; however, they also face challenges, including geopolitical risks, high transaction costs, and financial mismanagement. Diaspora investors prefer US dollar-denominated assets and shorter maturity periods. Outward remittances are increasing as Indians invest globally, but they can deplete India’s foreign exchange reserves if not managed carefully. Striking the right balance requires robust regulation and continued reforms to make investment easier, safer, and more attractive.
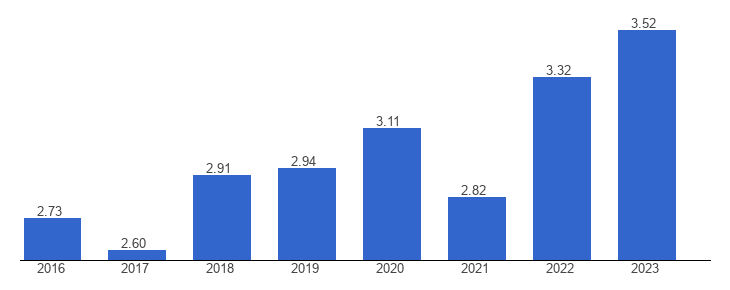
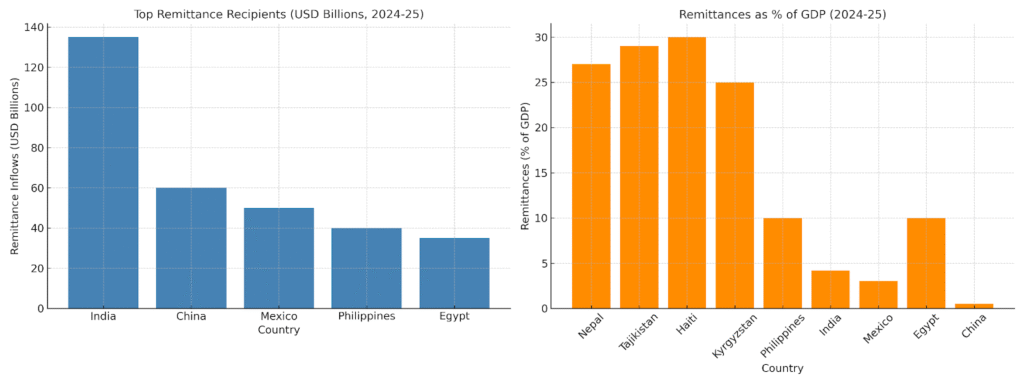
India remains the largest absolute recipient of remittances, receiving over $135 billion in FY 2024-25, equivalent to roughly 4–4.5% of its GDP. Indian remittances mainly originate from advanced economies such as the US (27.7% share) and the UAE (19.2%).
How Much Money in What Timeline?
1990s-2000: Remittances begin to rise rapidly, fueled by migration to the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, primarily for unskilled and semi-skilled labor. Remittance volumes surpass foreign aid, becoming one of India’s top external income sources.
2010: India becomes the world’s leading recipient of international remittances, supported by migrant labor in Gulf states and growth in skilled migration to Western nations.
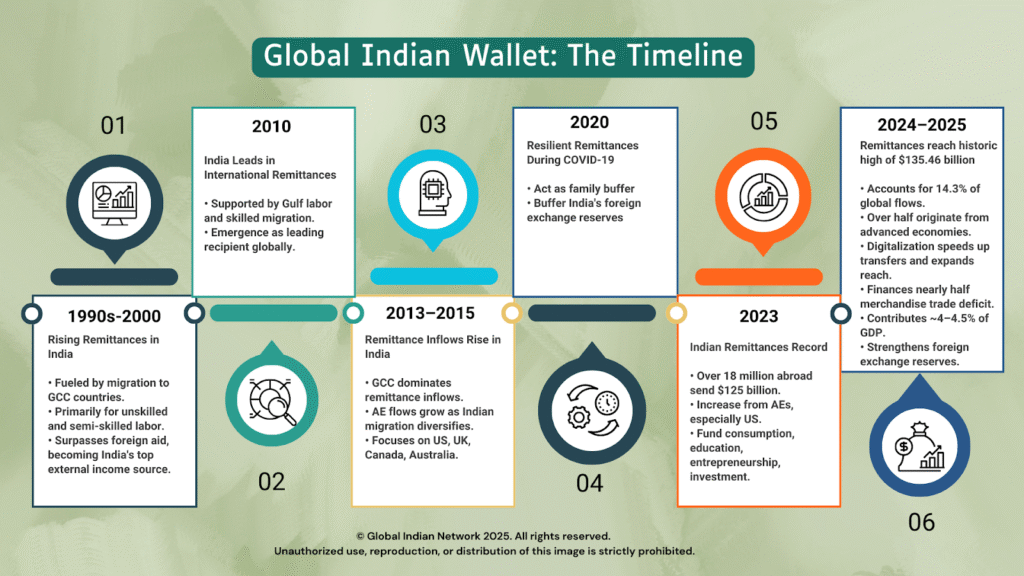
2013–2015: Significant rise in remittance inflows, with the GCC still dominant. However, flows from advanced economies (AEs) begin to grow as Indian migration diversifies toward the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
2020: Remittances prove resilient during the COVID-19 pandemic, acting as a buffer for families and India’s foreign exchange reserves despite global disruptions.
The world average remittance-to-GDP ratio is 5.13%, based on 174 countries.
2023: Over 18 million Indians abroad send a record $125 billion in remittances. The share from AEs—especially the US—surges, reflecting rising skilled migration and higher wages overseas. Remittances now fund consumption, education, entrepreneurship, and investment.
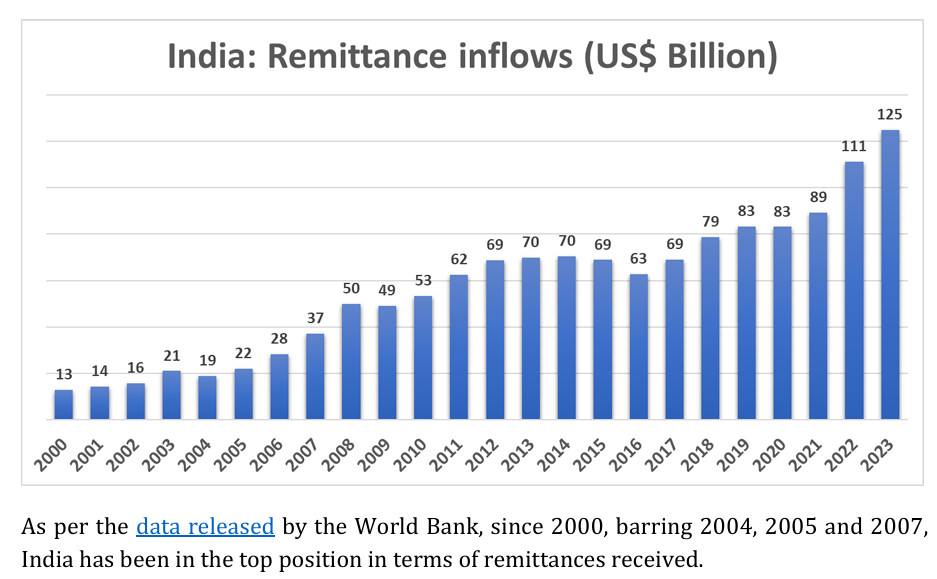
2024–2025: Remittances reach a historic high of $135.46 billion in FY 2024-25, accounting for 14.3% of global flows. Over half of remittances originate from advanced economies, surpassing GCC contributions for the first time. Digitalization speeds up transfers and further expands reach. This statistic captures both scale and global leadership, highlighting the diaspora’s profound financial impact on India’s development and economic stability.
2030 (projected): Remittance inflows may top $160 billion—driven by digital innovation, continued growth of the Indian diaspora in OECD countries, and policies that channel remittances into productive investments and entrepreneurship.
Where is the Regional Impact?
States like Maharashtra (20.5%), Kerala (19.7%), and Tamil Nadu (10.4%) receive exceptionally high remittance inflows, creating economic clusters deeply tied to migratory patterns. Here, remittances have transformed local economies, driving construction, small business development, and higher standards of living.

Are Remittances the Lifeblood of Families and the Economy?
The sheer magnitude of the inflows has a profound effect at both the micro and macro levels. For millions of households, remittances fund basic needs such as education, healthcare, and housing, boosting consumption, reducing poverty, and enhancing living standards, especially in rural regions.
At a national scale, these funds help stabilize India’s current account deficit, bolster foreign exchange reserves (recently touching $640 billion), and reduce dependency on foreign aid or volatile FDI flows. Remittances also offer resilience during crises—such as global economic downturns or natural disasters—enabling Indian families and local economies to weather uncertainties with greater confidence.
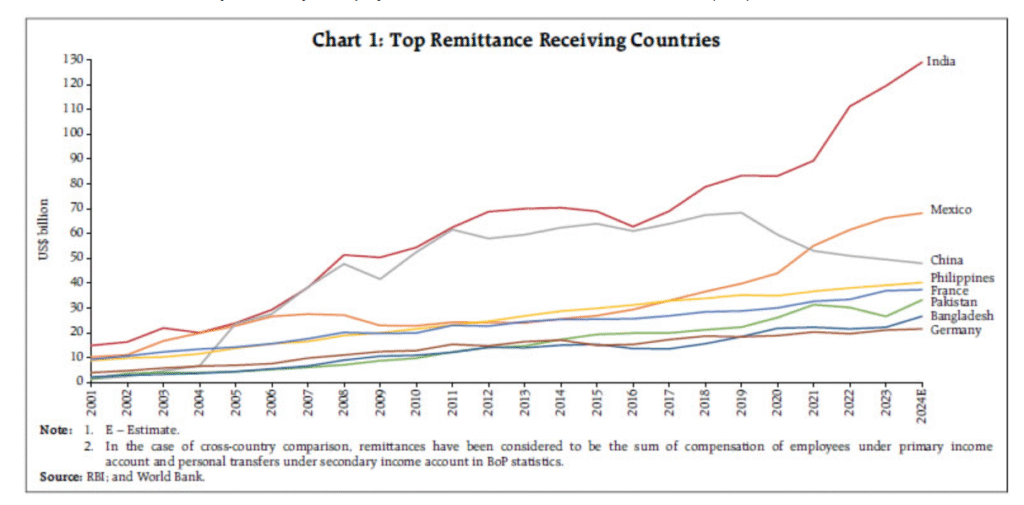
What are the Impacts of Diaspora Investments?
The Indian diaspora is attracting investments from Non-resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) into India’s capital markets, startup ecosystem, infrastructure, real estate, and emerging sectors. Recent reforms, digital platforms, relaxed repatriation rules, and transparency policies have made it easier for NRIs to invest in India. NRI deposits in Indian banks have doubled in recent years.
Gendered Remittance Flows
Indian women are transforming remittance narratives as strategic investors and community builders, prioritizing education, healthcare, and social upliftment. They are driving inclusive innovation through ventures like fintech platforms and ethical fashion brands. These entrepreneurs blend cultural insight with global acumen, channeling capital into impact-first models. Recognizing and amplifying their role is crucial for democratizing the “global Indian wallet,” reflecting gender equity, care-driven investment, and transnational solidarity.
How Does Diaspora FDI Compare to Remittance Flows for Impact?
Diaspora remittances and diaspora foreign direct investment (FDI) both significantly impact the economy, but in different ways. Remittances tend to be larger in volume and more stable over time, providing a steady inflow that directly supports household consumption, poverty reduction, and economic resilience—especially during downturns. For India, remittances contribute around 3-4% of GDP, surpassing both foreign aid and diaspora FDI flows in sheer size.
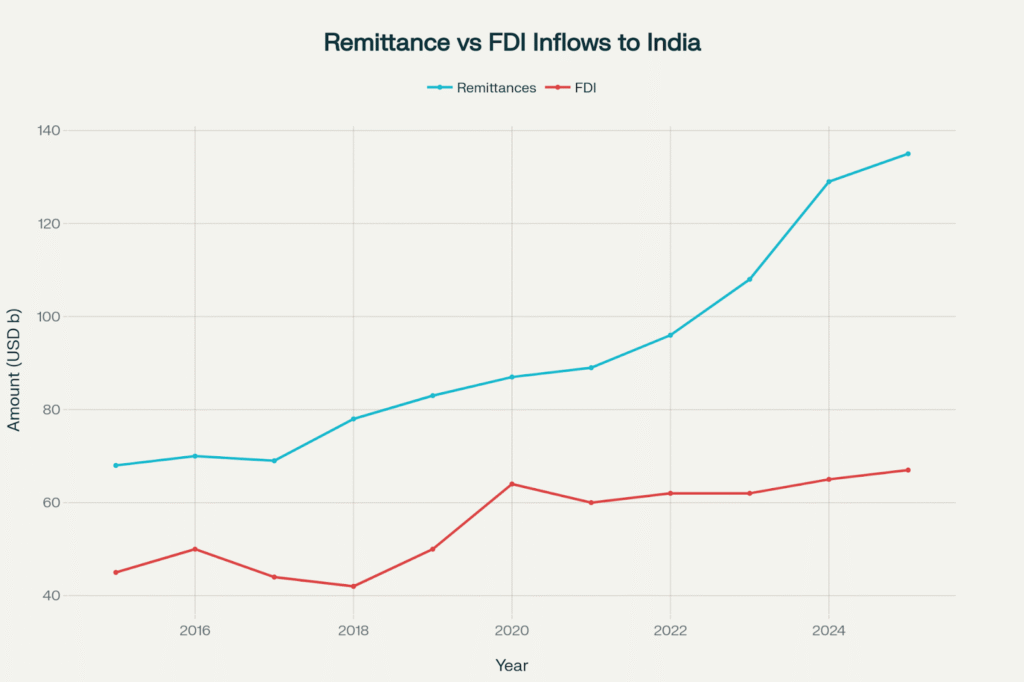
Diaspora FDI, although smaller in volume, has a significant impact on economic growth through capital formation, job creation, technology transfer, and infrastructure development. It is more volatile and sensitive to economic conditions. Remittances focus on legal migration and global mobility for Indian talent, while diaspora FDI catalyzes structural economic transformation and growth.
How Do Remittances Affect India’s Foreign Exchange Reserves?
Remittances are crucial for India’s foreign exchange reserves, as they boost the country’s foreign exchange reserves and reduce its dependence on external borrowings. India’s annual inward remittances, which exceeded $129 billion in 2024, finance nearly half of its merchandise trade deficit and provide a buffer against external economic shocks. Remittances also help India cover imports, service debt, and manage its balance of payments efficiently. The Reserve Bank of India recognizes remittances as the second-largest source of external financing. Remittances finance nearly half the merchandise trade deficit and contribute to GDP, strengthening foreign exchange reserves (over $640–677 billion).
Remittances also help India cover imports, service debt, and manage its balance of payments efficiently. The Reserve Bank of India recognizes remittances as the second-largest source of external financing.
Returnee Entrepreneurs
Is there anything beyond money?
Yes, of course. Some invaluable aspects include knowledge, innovation, and social capital.
Indian professionals abroad, particularly in high-value sectors such as IT, engineering, and healthcare, are transforming India into a global talent hub. They bring advanced skills, technology, and business practices, boosting local entrepreneurship and productivity. Indian diaspora-led businesses, like ArcelorMittal, have played transformative roles.
Returnee entrepreneurs often collaborate with domestic firms to overcome local challenges, introducing innovative products in tech and manufacturing sectors. 78% of government-funded Indian scholars return home, enhancing India’s talent ecosystem.
Real-World Case Studies
Returnee entrepreneurs from the Indian diaspora have profoundly shaped India’s startup and innovation landscape. For example, Sachin and Binny Bansal, who founded Flipkart after returning from the US, revolutionized e-commerce in India. Sridhar Vembu, founder of Zoho Corporation, returned to India from the US to build a global software company rooted in the country. Bhavish Aggarwal of Ola leveraged diaspora experience to challenge global ride-hailing markets.
Additionally, Nandan Nilekani’s leadership at Infosys, co-founded by NRI entrepreneurs, exemplifies the impact of the tech diaspora. These entrepreneurs blend global expertise with local insights, driving job creation, technology transfer, and economic growth, inspiring a new generation of innovators. They have leveraged diaspora networks, venture capital, and a combination of global and local knowledge to scale their businesses.
Diaspora-Led Climate or Tech Initiatives
The Indian diaspora is increasingly channeling its wealth, expertise, and networks into climate resilience and tech innovation—redefining remittances as strategic investments in India’s future.
Climate Innovation & Green Financing
IREDA & Diaspora Green Bonds: At the 2025 Pravasi Bharatiya Divas, Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA) showcased its $28.6B green financing portfolio, inviting diaspora investors to co-fund India’s renewable energy goals.
Indiaspora SDG Philanthropy: Diaspora philanthropy is projected to contribute $1.5–2.5B annually by 2030, rivaling India’s total foreign aid receipts. Funds are being directed toward clean energy, disaster resilience, and climate education.
Tech Leadership & Knowledge Transfer
Silicon Valley–India Tech Bridges: Leaders like Sundar Pichai (Google) and Satya Nadella (Microsoft) have invested in Indian R&D hubs, creating jobs and mentoring startups
Collaborative Hubs: Diaspora-founded incubators in the US and UK are partnering with Indian universities to foster innovation in EVs, medtech, and climate tech.
Expert Statements
“The diaspora is not just a remittance engine—it’s a sustainability partner,” said Pradip Kumar Das, CMD of IREDA.
“Our diaspora tech leaders are India’s unofficial STEM diplomats,” note Krishnan & Dayasindhu in ThePrint, urging policy support for AI, quantum, and green tech collaborations.
What is the Road Ahead?
As India’s global stature rises—marked by inclusion in major bond indexes and surging UPI digital transactions—the 2025 budget and policy landscape reflect growing ambition: streamlining residency and property rules for NRIs, digitalizing compliance, and incentivizing investment in infrastructure and startups. Facilitating the global Indian wallet’s flow through reduced paperwork, increased transparency, and innovative financial products promises to convert diaspora wealth into lasting development—fueling not only GDP growth but also social advancement and global influence.

Conclusion
The global Indian wallet, primarily driven by remittances and diaspora investments, has become a significant force in India’s economic trajectory, shaping fiscal policy, driving innovation, and stabilizing growth. Its impact extends beyond remittances, influencing household well-being, macroeconomic strength, capital markets, and technology transfer, demonstrating that remittances are just the beginning of a larger story.
As new generations of NRIs and overseas Indians adapt, they create vital channels for growth, partnership, and shared progress. Harnessing this transnational energy will be crucial for India’s future economic transformation.
The story of the global Indian wallet is a testament to the fact that when money is blended with knowledge and a deep connection to one’s roots, it becomes an unstoppable force for positive change, driving a new era of innovation and global influence for India. And pray, why would you not want to be a part of this?This article and the upcoming ones throw open a box of opportunities for the Indian entrepreneurs—notwithstanding where they reside. Follow us at Global Indian Network for further revelations.
FAQs
Why do the US Indian diaspora remittances translate into entrepreneurial growth abroad?
The US’s dominance is due to the high earnings of skilled Indians, making it the top country for both gross remittance flows and the economic impact. This dominance is attributed to the high earnings of skilled Indians.
Indian diaspora remittances offer a financial cushion for entrepreneurial risks and investments, fostering trust and networks within migrant communities. They also facilitate small-scale entrepreneurship using diaspora resources, serving as bridges between home and host economies for trade, knowledge transfer, and transnational innovation. These remittances create a thriving ecosystem abroad by providing capital, community networks, and access to knowledge and markets.
What policy tools most boost remittance-funded entrepreneurship?
The most effective policy tools to boost remittance-funded entrepreneurship include:
Reducing transaction costs of remittances through regulatory reforms, increased competition among remittance service providers, and the adoption of digital transfer technologies. Lower costs encourage more frequent and larger remittance flows, which are usable for business investments.
Improving access to formal financial services for remittance recipients, such as credit, savings accounts, and microfinance. This enables recipients to convert funds into productive ventures rather than just consumption.
Providing business development support, including entrepreneurship training, mentorship, technical assistance, and financial literacy programs to empower recipients in managing and growing their enterprises effectively.
Creating enabling regulatory environments with policies like tax incentives for remittance-funded startups, streamlined business registration processes, and support for women’s entrepreneurship, which help overcome structural barriers.
Supporting diaspora engagement and investment channels such as diaspora bonds, matching grants, and targeted credit to mobilize remittance capital at scale for local development and entrepreneurship.
Together, these tools transform remittances from consumption support into sustainable drivers of economic growth through entrepreneurships.
What explains the shift from GCC to advanced economies as top remittance sources?
Indian migrants are shifting to advanced economies like the US, UK, Canada, Australia, and Singapore due to better job opportunities, higher wages, and stable labor markets.
Gulf countries’ labor-nationalization’ policies, such as Saudi Arabia’s Nitaqat program, prioritize local employment over foreign workers, reducing opportunities for Indian migrants and lowering remittances from the GCC. Advanced economies attract skilled Indian professionals in STEM, finance, and healthcare sectors, who remit larger amounts. Policies like the India-UK Migration and Mobility Partnership facilitate easier movement and employment for Indian migrants, further boosting remittances.
Together, these factors have contributed to advanced economies surpassing the GCC in remittance contributions to India, indicating a structural shift in migration and economic patterns.