Conventional agriculture has always prioritized better yields in a short period but has not taken into account ecological sustainability. Therefore, sustainable agriculture is important, as it not only ensures food security but also reduces carbon emissions and pollution. By using green manure and reducing organic waste, sustainable agriculture is environmentally and economically viable.

However, a lingering question remains: Are there any challenges associated with sustainable agriculture? If any, what are these challenges?
Table of Contents
What is Meant By Sustainable Agriculture?

Sustainable agriculture means farming without harming the environment. It is a farming practice that makes optimum use of non-renewable resources but does not compromise human food and fibre needs. As a result, environmental quality is enhanced, thus improving the lives of farmers and society at large.

Why is Sustainable Agriculture Better Than Conventional Agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture is better than conventional agriculture because it provides a holistic approach to farming. It maintains sufficient crop yields and ecological balance, healthy soil, and biodiversity, in addition to ensuring economic viability.
Conversely, conventional farming practices focus on maximizing crop yields by using chemical fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides, which cause soil degradation. Conventional agriculture ensures economic growth as it focuses on a single crop, which reduces labour costs and is easy to harvest. However, this causes environmental damage and loss of biodiversity.

Sustainable farming methods play a crucial role in long-term sustainability by reducing the use of synthetic fertilizers and practising crop rotation. These methods ensure crop yields and soil health compared to traditional farming methods. Sustainable farming also maintains carbon in the soil.
What is the Future of Sustainable Agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture practice is the future of the agriculture sector because, within it, natural ecosystems and economic sustainability can go hand in hand. With the advancement of technology, agricultural sustainability can see a bright future. These technologies are-
- Artificial Intelligence: AI helps farmers analyze the timings to plant crops and feed livestock by meeting the best price in the market. It can also help farmers to determine systematic spraying of fertilizers.
- Biotechnology: Sophisticated modern technology has made it easier to crossbreed plants in less time. Even modifications in adding or removing characteristics to the crops can be done easily through biotechnology.
- Drones: Farmers use drones to spray organic fertilizers on crops and take aerial pictures that help them assess the crops. Moreover, drone sensors can capture data regarding crop health and weed growth.
- Blockchain Technology: Though it is associated with cryptocurrencies, it can help to track transactions both securely and accurately.
- Crop per drop Initiative: Adopting conservation tillage, modern genetics, and drip irrigation will help initiate ‘crop per drop‘. This agricultural policy ensures both soil and water quality. Due to increasing water pollution and reduced water bodies, this sustainability orientation ensures water resources from further depletion as well as soil quality.

Whatever technologies are used for future developments in sustainable agriculture, they must be available to farmers who are not so rich. This will ultimately contribute to our sustainable future and biodiversity conservation.
What are the Challenges Associated with Sustainable Agriculture?
Though sustainable farming methods are the future of the agricultural sector, they are also fraught with challenges. Let us learn what the challenges associated with sustainable agriculture are.
- Adaptation: It is indeed difficult for farmers to change from conventional, high-yielding farming methods to organic farming, which is time-consuming. Even the transition period itself will cause temporary setbacks in earning profits, food security and income.
- Economic burden: Organic farming will take time to achieve economic resilience. The initial investment required for new practices and agricultural technologies will be a significant challenge.
- Variations in Agricultural Output: When farmers transition, sustainable agricultural practices can lead to fluctuations in agricultural output. This can negatively impact poor farmers, who solely depend on agricultural production.
- Access to Knowledge: Access to knowledge about sustainable practices is a challenge because agricultural extension services are limited in remote areas.
- Limited Organic Inputs: The limited availability and high prices of organic fertilizers and pesticides challenge sustainable agricultural development.
- Obtaining Certification and Market Demand: Obtaining and maintaining certificates is a challenge, as it is a complex and costly process. Market fluctuations and access to sustainable products are also hindrances.
- Pest Management: Since sustainable food systems depend on non-chemical methods and Integrated Pest Management (IPM), they require consistent management, which would require many labourers. This might not be a profitable solution for farmer networks in the long run.
- Limited Suitability: Some unsustainable practices might not apply to all crops. Crop rotation and organic agriculture are limited to certain types of crops.
- Climate Crisis: Irregular rainfall systems, excessive floods, and drastic changes in temperature affect agricultural systems. Therefore, farmers in developing countries need to be agile while adopting sustainable farming to ensure constant food supplies.
- Increasing Population: Considering recent population growth, meeting a wide range of constant food demands is a challenge. This is because sustainable agriculture provides less yield than conventional agriculture.

What are the Opportunities Associated with Sustainable Agriculture in the US?
The US is leading the world in sustainable agricultural production. By providing reasonably priced food, it can meet the growing demands of its citizens and people worldwide. The US is also an example of maintaining a constant food supply chain, as it ensures food security in times of conflict or economic disruptions.
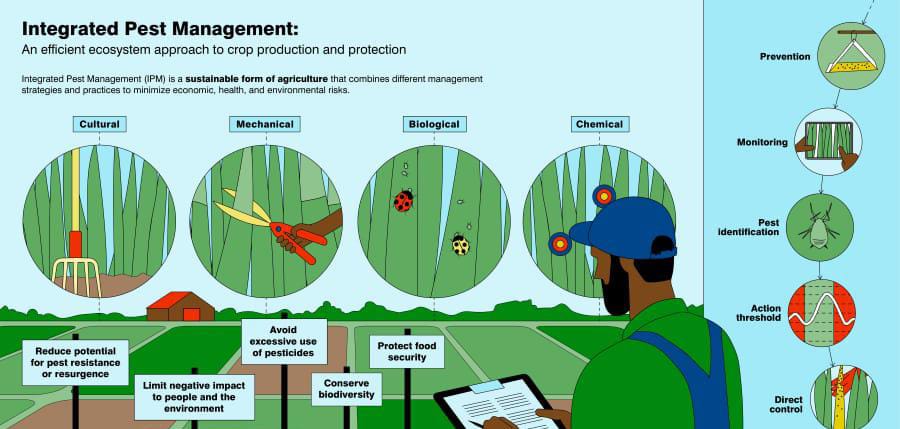
Some of the innovative solutions and opportunities which are associated with sustainable agriculture in the US are:
- Farm and ranch practices.
- Integrated Pest Management system (IPM).
- Rotational Grazing.
- Soil Conservation.
- Water conservation and protection of wetlands by incorporating practices such as riparian buffer strips.
- Cover crops.
- Landscape diversity.
- Nutrient management.
- Agro-forestry.
- Innovative marketing strategies.
All these not only ensure carbon soil storage and soil structure but also prevent biodiversity loss.
What are the Challenges Associated with Sustainable Agriculture in the US?
Though the US provides the best model, there are still challenges associated with sustainable agriculture. These can be listed as follows:
- Public measures are not well connected within sectors for new farmers’ networks.
- Farmers, especially new farmers, do not receive adequate responses from legislators when needed if they are involved in industrial agriculture.
- There is a lack of funding for farmer assistance programs, and hence, they are unable to reach large numbers—for example, USDA’s Environmental Quality Program.
- Non-utilization of federal programs in states that do not support progressive public services for farmers. Some federal programs, subnational programs and NGO programs are limited in their scope as they cover certain states.
- Lack of adequate knowledge, rules and accountability are not put into practice.

Apart from these, enlisted are some future challenges that the US agricultural system might face if it does not make informed choices to make efficient solutions.
- Diminished margins of return, making farm incomes volatile.
- Instead of the government, international trade organizations and NGOs will control food regulations.
- A continuous shift from farming to agri-business.
- US consumers will have increased consumption of animal protein.
- Rural countries of the US will become urbanized.
- Increase in the medicalization of agriculture.
RELATED: Maximizing the Economic Impact of Sustainable Agriculture
Conclusion
Despite the challenges associated with sustainable agriculture, it is the only viable option for ensuring sustainable development. Sustainable agriculture includes conservation agriculture, intensive agriculture, and precision agriculture, which not only ensures soil resilience, fresh water, and greenhouse gas emissions but also equal access to resources and food. This initiative of greener agriculture plays a central role in encouraging friendly practices to minimize environmental impact.

FAQs
What Is the Meaning of Sustainable Food?
A sustainable food system ensures that food is produced in such a manner that it meets nutrition quality standards and provides equal access to food, even in times of emergency.
What Are the Challenges for Sustainable Agriculture?
The challenges of sustainable agriculture include adaptation to sustainable farming methods, economic burden, variation in agricultural output, and lack of access to knowledge.
How can Food Sustainability Be Improved?
Food sustainability is directly linked with agricultural sustainability. Therefore, agricultural sustainability needs to be improved by giving economic opportunities to poor farmers so that they can adopt climate-smart agriculture.










[…] of the most basic principles of sustainable agriculture is the adoption of sustainable agricultural activities that reduce the environmental footprint of […]
[…] National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), was designed to ensure sustainable development in agriculture by promoting efficient farming practices, resource management, and adaptive strategies to mitigate […]
[…] is another important factor in ecological integrity, which includes waste and resource minimizing, sustainable agriculture, and forestry and fishery practices. It encourages the creation of renewable energy sources, […]